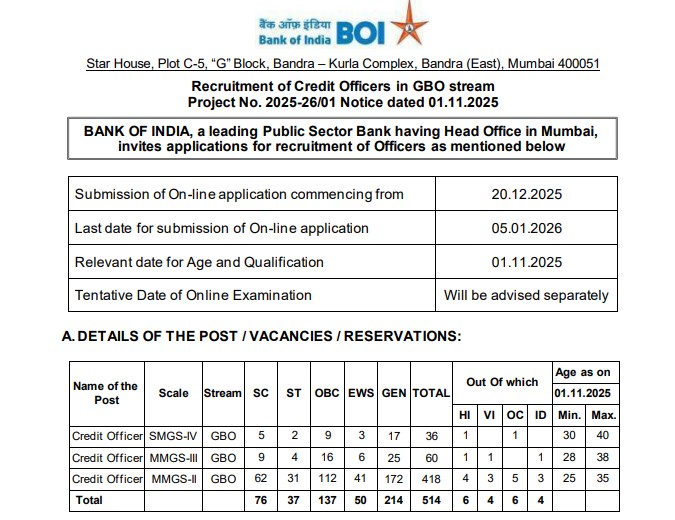
Anudip Foundation for Social Welfare, in collaboration with DBS Bank India, has opened a DeepTech Training Centre in Airoli, Navi Mumbai. The centre forms part of a three-year skilling programme designed to train and empower 2,400 youth from underserved communities across Mumbai, Kolkata, Pune and Chennai. The initiative focuses on equipping young learners with industry-relevant, future-ready technology skills, helping them prepare for emerging roles in the fast-evolving digital economy.
I am writing about this initiative because skill-based education, especially in advanced technology areas, can be a real turning point for young people who otherwise have limited access to such opportunities. While conversations around technology often focus on innovation and growth, they sometimes miss the human side—who actually gets access to these opportunities. This DeepTech Training Centre is important because it bridges that gap. It combines corporate support with grassroots experience to ensure that students from marginalised backgrounds are not left behind as the job market evolves. By highlighting this collaboration, the aim is to show how targeted training programmes can create long-term impact, not just for individuals but also for the broader economy.
About the DeepTech Training Centre
The newly inaugurated centre at Airoli has been designed as a hands-on learning space where students can gain practical exposure to emerging technologies. The training programmes are aligned with current industry needs, ensuring that learners are job-ready by the end of the course.
The centre is part of a larger plan to reach 2,400 beneficiaries over three years, with training hubs spread across four major cities.
Technologies and Skills Being Taught
The DeepTech Training Centre focuses on high-demand technology areas that offer strong employment potential. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning fundamentals
- Data analytics and data-driven decision-making
- Cloud computing basics
- Digital and financial technology tools
- Workplace readiness and professional skills
Along with technical training, students also receive support in communication, problem-solving and interview preparation.
Who Will Benefit from This Initiative
The programme is aimed at young individuals from underserved and economically weaker backgrounds. Priority is given to:
- First-generation learners
- Youth from low-income households
- Students with limited access to formal tech education
- Job seekers looking to upskill or reskill
By focusing on inclusion, the programme ensures that talent is not limited by social or financial barriers.
Role of Anudip Foundation
Anudip Foundation brings years of experience in skill development and livelihood programmes. The organisation has worked extensively with marginalised communities, helping youth transition into sustainable employment.
At this centre, Anudip is responsible for:
- Curriculum delivery and training management
- Student mobilisation and mentoring
- Continuous assessment and performance tracking
- Placement support and industry linkages
Their community-level understanding plays a key role in student retention and success.
Role of DBS Bank India
DBS Bank India is supporting the initiative as part of its commitment to social impact and inclusive growth. Through this partnership, the bank is contributing to:
- Funding and infrastructure support
- Strategic guidance for programme design
- Long-term planning for scalability
- Strengthening employability outcomes
Such collaborations show how corporate participation can go beyond funding and actively support workforce development.
Expected Impact Over Three Years
Over the next three years, the initiative aims to:
- Train 2,400 young people across four cities
- Improve access to high-quality tech education
- Increase employment and income opportunities
- Create a pool of skilled talent for the digital economy
- Promote diversity and inclusion in the tech workforce
Graduates of the programme are expected to find roles in entry-level tech, data and digital operations across sectors.
Why DeepTech Skills Matter Today
As industries adopt automation, data-driven systems and AI-based tools, demand for tech-skilled professionals continues to rise. However, access to such training is often limited to a small section of society.
Initiatives like this are important because they:
- Prepare youth for future job markets
- Reduce skill gaps in the technology sector
- Support inclusive economic growth
- Enable social mobility through employment
By investing in people, the programme creates value that goes beyond immediate job placements.