Chapter 12 of NCERT Class 12 Mathematics is about Linear Programming, a very practical and scoring chapter. It teaches students how to find the best possible outcome (like maximum profit or minimum cost) by applying mathematical techniques. This chapter is all about formulating problems based on real-life situations and solving them using graph-based methods. It mainly includes linear inequalities, constraints, objective functions, and feasible solutions. Even though the graphs are simple, understanding how to read them correctly is the key.
I chose to write on this chapter because many students take it lightly, thinking it’s just about drawing graphs. But the real challenge lies in writing the correct inequalities from word problems and identifying the feasible region properly. Linear Programming has high application in business, supply chain, operations, and economics. Even in competitive exams like JEE (Main), CUET, or NDA, questions come directly from this chapter. It’s also one of the easiest topics to score full marks in the Class 12 board exam. That’s why it’s important to learn the concepts clearly and use the NCERT PDF regularly for practice.
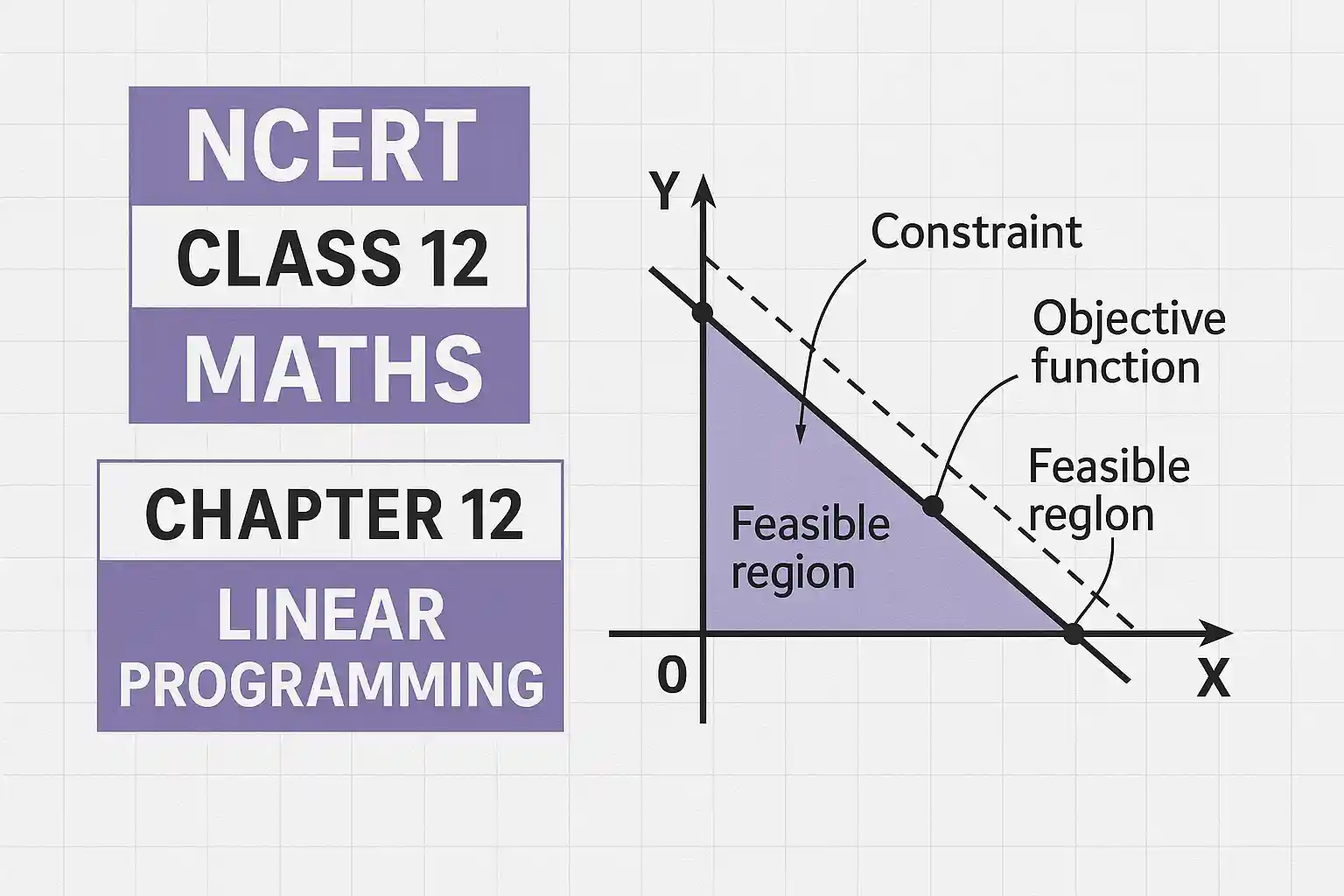
What is Linear Programming?
Linear Programming (LP) is a method used to optimise (maximize or minimize) a particular quantity, usually profit or cost, under given constraints. In simple terms, LP helps us to take the best decision when there are limited resources and multiple conditions to satisfy.
Key Terms You Need to Know
- Objective Function: The function to be optimised (like
z = ax + by) - Constraints: The conditions given in the problem as inequalities
- Feasible Region: The region that satisfies all the constraints
- Bounded Region: A region that is closed on all sides
- Optimal Solution: The point in the feasible region where the objective function is maximum or minimum
Types of Linear Programming Problems Covered
In NCERT, three types of problems are mostly discussed:
- Diet Problem – Minimising cost of food with given nutrition constraints
- Manufacturing Problem – Maximising profit with limited resources
- Transportation Problem – Finding the cheapest or shortest route for delivery
These are presented in the form of word problems and have to be converted into mathematical inequalities and solved by drawing graphs.
Step-by-Step Method to Solve LPP
Here is a simple way to solve any Linear Programming Problem in exams:
- Identify the variables (usually x and y)
- Write the constraints as linear inequalities
- Plot the inequalities on a graph to find the feasible region
- Write the objective function
- Find corner points of the feasible region
- Substitute corner points in the objective function to get the optimal value
Why This Chapter is Scoring and Useful
What I like most about this chapter is that it’s completely application-based. If you know how to draw basic linear graphs and find intersection points, you’re already halfway there. Most CBSE papers ask 5-mark questions from this topic, and students can easily score full marks if they follow the method step-by-step.
Also, the real-world examples make this chapter more relatable. From choosing the best production method to optimising a delivery route, LP is everywhere. Many commerce and engineering students use these concepts later in their professional studies, especially in management, economics, and logistics.
Download NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming PDF
To revise this chapter anytime, it’s helpful to have the official PDF with you.