The NCERT Class 12 Microeconomics Chapter 4 titled The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition talks about how firms behave when there is perfect competition in the market. This chapter explains concepts like revenue, cost, market supply, and equilibrium. It helps students understand how firms take decisions on pricing and output when there are many sellers selling identical products.
I’m writing about this chapter because it is one of the most important chapters for students preparing for their board exams or competitive exams like CUET, DUET, etc. A lot of students struggle with economic theory, especially when it comes to perfect competition, so having a simple explanation and access to the official PDF can make a big difference. Also, this chapter builds the foundation for understanding real-world market structures. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or parent, knowing the basics of how firms operate in such conditions is important. That’s why I’m also sharing the direct link to download the PDF from the official source, so you get authentic and updated content without confusion.
What is Perfect Competition?
Perfect competition is a market structure where there are many sellers, all selling identical products. No single firm can influence the price, and buyers have full information. Some key features of perfect competition include:
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous products
- Free entry and exit
- Perfect knowledge of market conditions
- No transport costs
Under such conditions, firms are price takers, meaning they accept the market price and cannot change it. If a seller tries to sell at a higher price, buyers will simply switch to another seller.
Key Concepts in Chapter 4
Here are the major topics covered in this chapter:
1. Revenue Concepts
- Total Revenue (TR): Price × Quantity sold
- Average Revenue (AR): Total Revenue ÷ Quantity
- Marginal Revenue (MR): Change in Total Revenue from selling one more unit
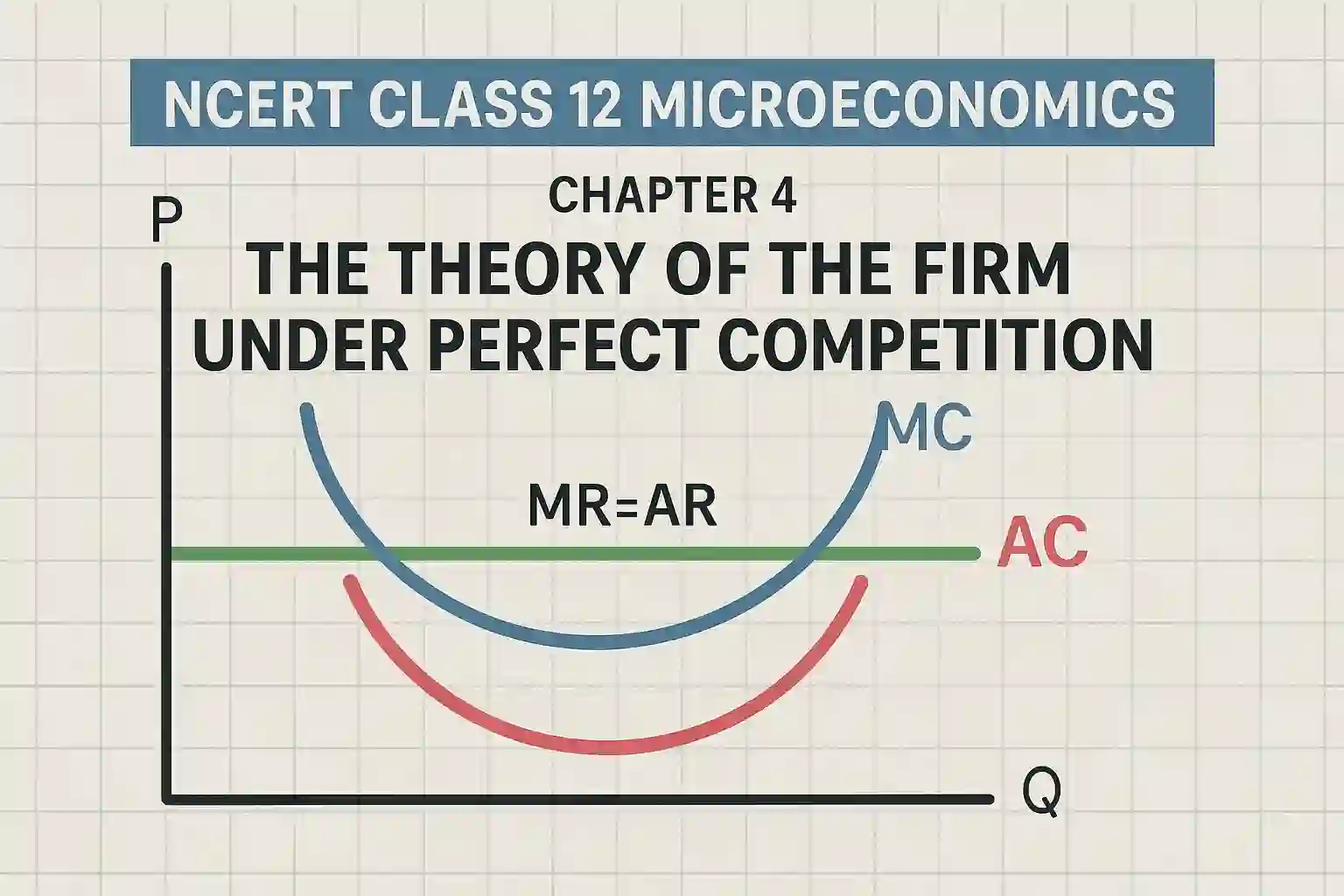
In perfect competition, AR = MR = Price. This is a very important concept for MCQs and understanding graphs.
2. Cost Concepts
Students are expected to understand different types of costs:
- Total Cost (TC)
- Average Cost (AC)
- Marginal Cost (MC)
The firm makes its production decisions based on the relation between MR and MC.
3. Profit Maximisation
In perfect competition, the firm maximises its profit where:
Marginal Cost = Marginal Revenue
This is the basic condition for equilibrium of a firm in the short run.
4. Short Run vs Long Run
- Short Run: At least one factor of production is fixed. The firm can make supernormal profits, normal profits or losses.
- Long Run: All factors are variable. Firms make only normal profits due to free entry and exit.
5. Supply Curve of the Firm
The supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm is the part of its Marginal Cost curve that lies above the Average Variable Cost.
Understanding the firm’s supply decision is key to solving numerical and graphical questions in exams.
Download NCERT Class 12 Microeconomics Chapter 4 PDF
You can download the official NCERT PDF for Chapter 4: The Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition from here. This is completely free and updated as per the latest syllabus.