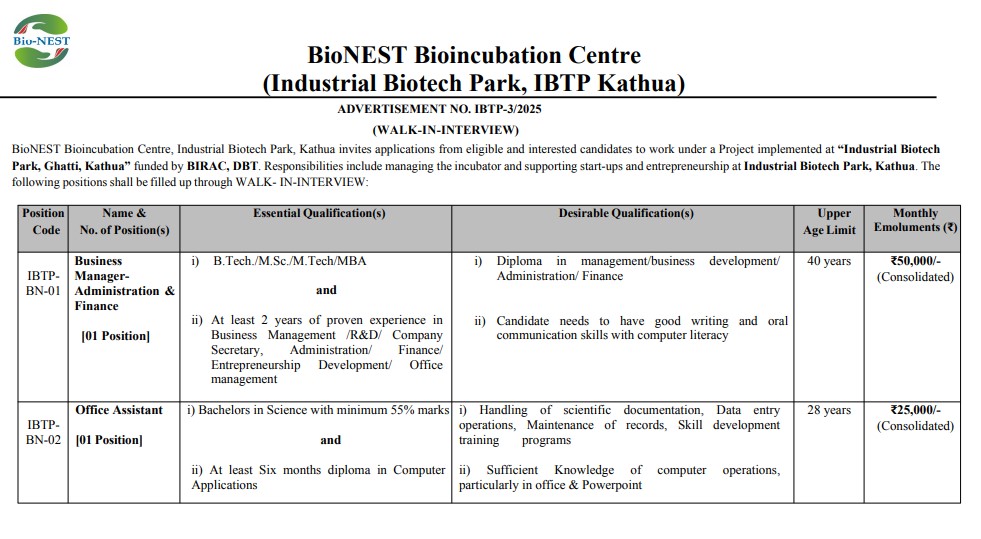
Chapter 8 of Class 11 Political Science Part 1 (Hindi Medium), titled धर्मनिरपेक्षता, explains the meaning of secularism and its role in a democratic society. This chapter discusses how the state should relate to religion and why maintaining distance from religious favouritism is essential for equality and freedom. It clarifies that secularism is not about being anti-religion, but about ensuring that no religion is given special status by the state and that every individual enjoys the freedom to follow their own beliefs.
I am writing about this chapter because secularism is often misunderstood, especially in public debates. Many students hear the term frequently but may not clearly understand what it truly stands for. This chapter helps break common myths by explaining secularism in a balanced and practical way. In a country like India, where people follow different religions, secularism plays a crucial role in maintaining harmony and mutual respect. Understanding this chapter helps students see why constitutional values matter and how secularism protects both religious freedom and social unity. It also encourages learners to think critically about how politics and religion should interact in a democracy.
About Chapter 8: धर्मनिरपेक्षता
This chapter explores the concept of secularism and why it is necessary in modern democratic states.
What Is Secularism?
Secularism refers to the principle that the state should not favour or discriminate against any religion. It ensures equal treatment of all religions and protects the right of individuals to practise, change, or not follow any religion.
Key ideas of secularism include:
- Equal respect for all religions
- Freedom of religious belief and practice
- Separation of religion from state power
- Protection of minority rights
Why Secularism Is Important
The chapter explains that without secularism, religious differences can turn into political conflicts. Secularism helps in:
- Preventing religious domination
- Ensuring equality before law
- Promoting peaceful coexistence
- Protecting individual freedom of conscience
It acts as a safeguard against discrimination and intolerance.
Secularism and the Indian Constitution
India follows a unique model of secularism. Instead of strict separation, the Indian state maintains principled distance from all religions.
This means:
- The state does not promote any religion
- It can intervene to prevent discrimination
- Religious freedom is guaranteed to all citizens
This approach respects diversity while maintaining equality.
Common Misunderstandings About Secularism
The chapter clears several misconceptions:
- Secularism does not mean rejection of religion
- It does not weaken faith
- It does not favour any single community
Instead, it creates space for all beliefs to coexist peacefully.
Secularism in Everyday Life
Secularism affects daily life through:
- Equal access to public institutions
- Freedom to celebrate religious festivals
- Protection from religious discrimination
- Fair laws applicable to all citizens
These principles help maintain social harmony in diverse societies.
NCERT Class 11 Political Science Chapter 8 PDF Download (Hindi Medium)
Students can download the official NCERT PDF by following these steps:
- Visit the official NCERT website
- Click on E-Books
- Select Class 11
- Choose Political Science
- Open Political Theory – Part 1 (Hindi Medium)
- Click on Chapter 8: धर्मनिरपेक्षता
- Download the PDF for study and revision
Always use the official NCERT source to ensure accurate and updated content.